Email queues handle communication between an email server and Daktela.
Create a New Email Queue/Edit Queue
To set up your email queues, go to Manage → Queues.
To create a new queue from scratch, click Add new and select Email.
To use an existing queue as a template for your new one, click Clone in the Actions column.
To edit an existing queue, click its title.
The queue details will open.
Email Queue Details
Fill out the Unique queue number, Title and Description (optional), then sign in to your email server and set up your queue.
Queue Number Auto-Suggestion
Daktela will automatically suggest the next available number based on previous numbers of the same queue type (including deleted ones).
For your email queue to send and receive email, you need to set up Incoming mail server and Outgoing mail SMTP server at the bottom of the queue settings.
Queue Field Details
Queue Field Details
Open more settings using the Extended button in the top right corner.
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Advanced settings |
|
|
Queue active |
By disabling the queue, you can quickly pause it.
|
|
Auto response |
Select a template to automatically send as a reply to all newly created tickets received using this queue. Will only be used during working hours if set up below. Go to Manage → Settings → Templates to set up your templates. |
|
Working hours |
Select your working hours from your Time groups. Go to Manage → Settings → Time groups to set up your Time groups. |
|
Sender info |
Title of sent email. Queue and user object can be used.
|
|
Sender address |
This address will appear as the sender’s address. Must be allowed on mail server! |
|
Reply-to header |
The email address to which replies should be sent. If left empty, replies will be sent to the default address. |
|
Signature template |
Select an Email signature template to automatically add to emails. Go to Manage → Settings → Templates to set up your templates. |
|
NPS survey template |
Template for adding Net Promoter Score surveys. Go to Manage → Settings → Templates to set up your templates. |
|
Postprocessing in event |
Warning: This is an advanced feature. When set up incorrectly, it will break outgoing emails in this queue.
|
|
Wrapup time |
Select the amount of time that needs to pass before a new activity can be routed to an agent that has just finished an activity (the length of the Wrap pause). |
|
Multiple statuses |
Allow or disallow users to set multiple statuses for activities using this queue. |
|
SSL Trusted |
Allow trusted certificates only. |
|
Helpdesk title |
Select the helpdesk for this queue. Contact Daktela Support to set up a helpdesk. |
|
Incoming mail server |
|
|
IMAP |
|
|
Protocol |
Select how you would like to authenticate communication with your email server. |
|
Server |
The server your email is located on. Contact your email provider to find your address. |
|
Name |
Your login name – usually the same as your email address. |
|
Password |
Your email login password. |
|
SSL |
Turn on to connect using SSL. |
|
Don't keep emails (Extended) |
Do you want to remove emails from the mail server after downloading them? |
|
POP3 |
|
|
Protocol |
Select how you would like to authenticate communication with your email server. |
|
Server |
The server your email is located on. Contact your email provider to find your address. |
|
Name |
Your login name – usually the same as your email address. |
|
Password |
Your email login password. |
|
SSL |
Turn on to connect using SSL. |
|
Do not keep emails |
Do you want to remove emails from the mail server after downloading them? |
|
IMAP + OAuth2 |
|
|
Protocol |
Select the protocol used to communicate with the email server (POP3 or IMAP, from 6.21+ Microsoft Office 365 OAuth2 or Google OAuth2). |
|
Use same method for Outgoing |
Use same settings (including token) for outgoing emails. One token is used for incoming & outgoing emails. |
|
Name |
Your login name – usually the same as your email address. |
|
Do not keep emails |
Do you want to remove emails from the mail server after downloading them? |
|
Google API + OAuth2 |
|
|
Protocol |
Select how you would like to authenticate communication with your email server. |
|
Use same method for Outgoing |
Use same settings (including token) for outgoing emails. One token is used for incoming & outgoing emails. |
|
Name |
Your login name – usually the same as your email address. |
|
Oauth provider |
Click the G button to authorise Gmail. |
|
Do not keep emails |
Do you want to remove emails from the mail server after downloading them? |
|
AzureAD GraphAPI + SSO |
|
|
Protocol |
Select how you would like to authenticate communication with your email server. |
|
Use same method for Outgoing |
Use same settings (including token) for outgoing emails. One token is used for incoming & outgoing emails. |
|
Name |
Your login name – usually the same as your email address. |
|
Oauth provider |
Click the Windows button to authorise email. |
|
AzureAD GraphAPI Tenant |
|
|
Protocol |
Select how you would like to authenticate communication with your email server. |
|
Use same method for Outgoing |
Use same settings (including token) for outgoing emails. One token is used for incoming & outgoing emails. |
|
Name |
Your login name – usually the same as your email address. |
|
Configuration |
You can find configuration in integrations. First of all you have to create the configuration in Integrations (External Libraries). |
|
Outgoing mail SMTP server |
|
|
SMTP server |
|
|
Protocol |
Select how you would like to authenticate communication with your email server. |
|
Server |
The server your email is located on. Contact your email provider to find your address. |
|
Name |
Your login name – usually the same as your email address. |
|
Password |
Your email login password. |
|
Port |
SMTP | Port 587 (Insecure Transport)
|
|
SMTP + OAuth2 |
|
|
Protocol |
Select how you would like to authenticate communication with your email server. |
|
Server |
The server your email is located on. Contact your email provider to find your address. |
|
Name |
Your login name – usually the same as your email address. |
|
Port |
SMTP | Port 587 (Insecure Transport)
|
|
Google API + OAuth2 |
|
|
Protocol |
Select how you would like to authenticate communication with your email server. |
|
Name |
Your login name – usually the same as your email address. |
|
Oauth provider |
Click the G button to authorise Gmail. |
|
AzureAD GraphAPI + SSO |
|
|
Protocol |
Select how you would like to authenticate communication with your email server. |
|
Name |
Your login name – usually the same as your email address. |
|
Oauth provider |
Click the Windows button to authorise email. |
|
Tickets |
|
|
Category |
Select a category that will automatically be assigned to tickets created in activities using this queue. |
|
Auto response exceptions |
Auto responses will not be sent to these email addresses – checks both "from" and "reply-to" fields. You can enter only domain or use wildcards * (for anything) and ? (for any character). |
|
AI Categorisation
|
Turn on to use AI to select the category that best fits your incoming emails based on your ticket history: activate smart routing. Select the categories that the AI can choose from in the Categories field below. If the AI is not confident enough of its selected category, the category selected in the Category field above will be used.
|
|
AI Statuses |
Turn on to use AI to select statuses that best fit your incoming emails based on your ticket history: activate smart routing. Select the statuses that the AI can choose from in the Statuses field below.
|
|
AI Template Suggestions |
Turn on to use AI to suggest the best fitting Templates to agents when they reply to emails.
|
Save your queue.
Don't forget to set up:
-
which Agents can use the queue.
-
the queue's relations.
-
the queue's widget scheme.
See Queues for instructions.
How to Authorise Gmail For Use With Daktela
How to Authorise Gmail For Use With Daktela
Incoming email
-
Under Incoming mail server, select the Google OAuth2 Protocol.
-
Enter your email address into the Name field.
-
Click the G button to authorise Gmail.
-
A new tab will open. Sign in to your Google Account.
-
Grant Daktela permission to access your Google Account. Make sure to check Read, compose and send emails from your Gmail account. Click Continue.
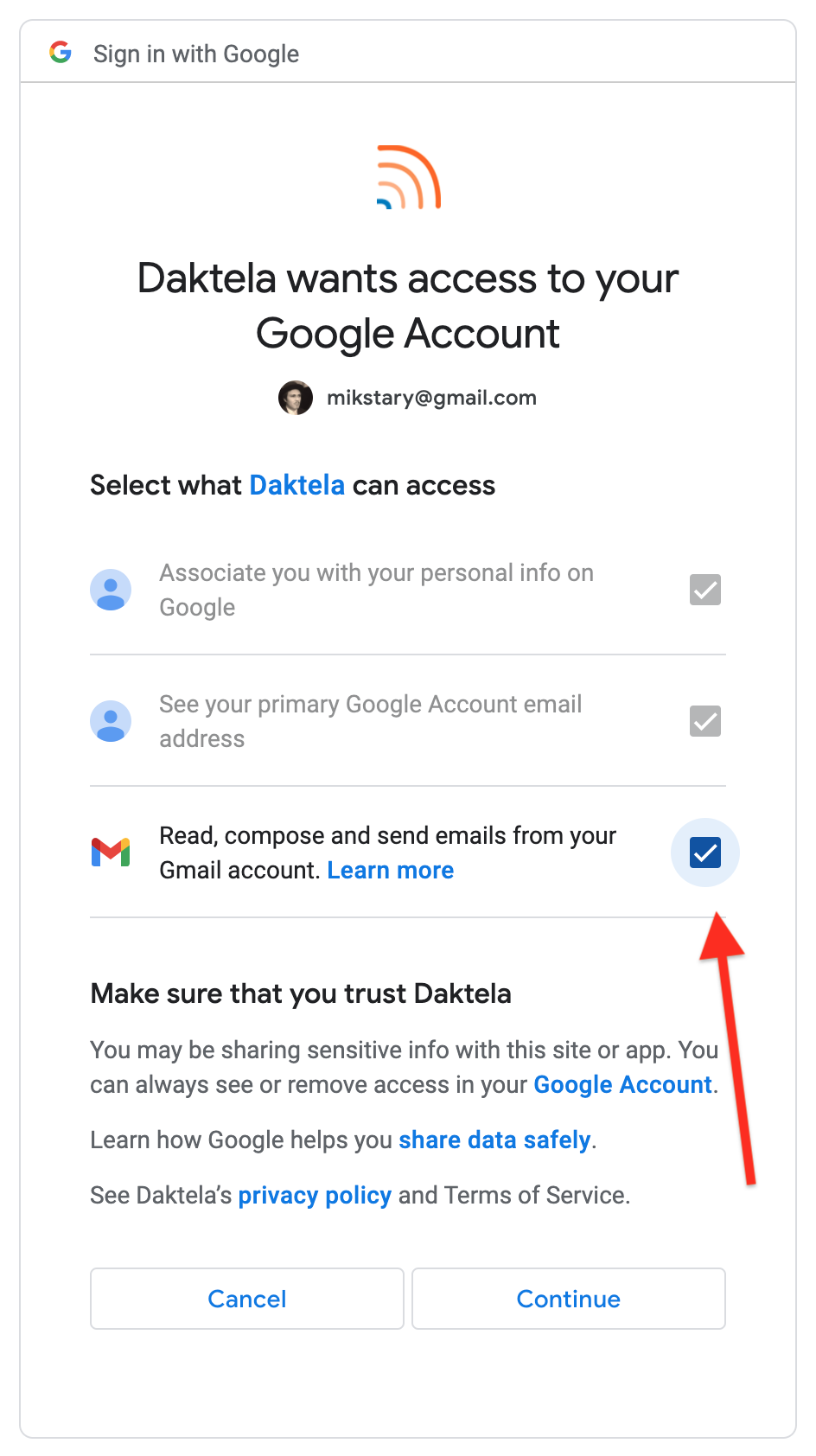
-
Outgoing email
Fill out the following under Outgoing mail SMTP server:
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Server |
smtp.gmail.com |
|
Name |
Enter your email address. |
|
Port |
Select 465 (Encrypted connection SSL). |
How to Authorise Microsoft Office 365 For Use With Daktela
How to Authorise Microsoft Office 365 For Use With Daktela
Incoming email
-
In the Incoming mail server section, select Microsoft Office 365 OAuth2 in the Protocol field.
-
Enter your email address into the Name field.
-
Click the MS window button to authorise your MS Account.
a. A new tab will open. Enter your email address and click Next to continue.%20-%20Copy.png?cb=0d3814be4f04c76dae4a0698c1545fd4)
b. Enter your password and click Sign in.
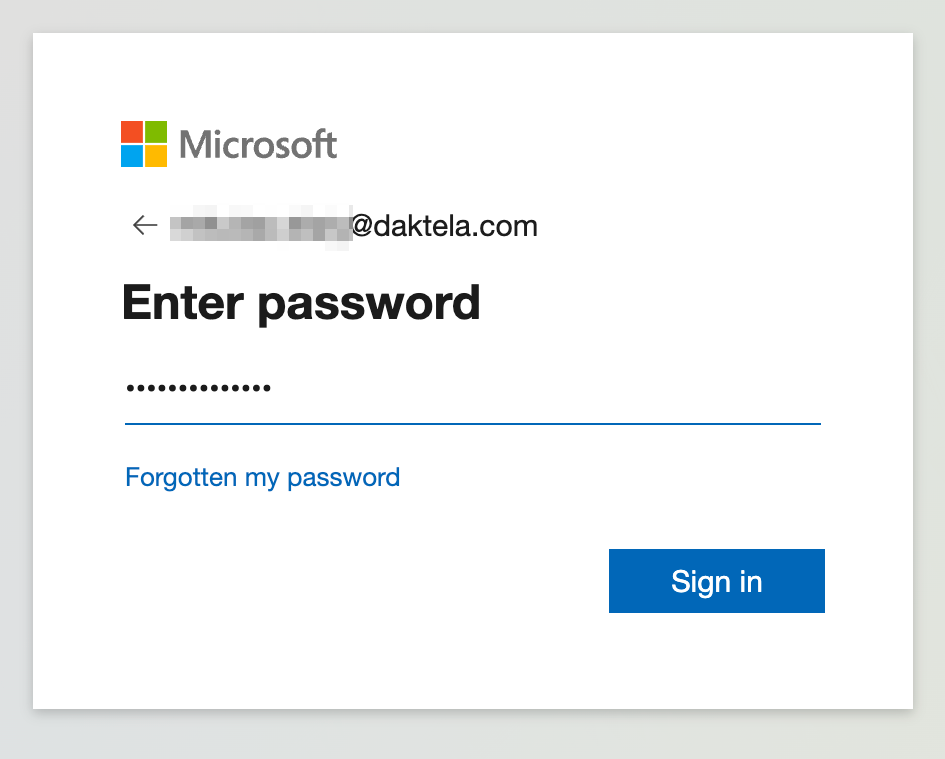
c. Click Yes to continue.
%20-%20Copy.png?cb=8c327fd9b8da947f810eba58efac81f2)
d. Finish the authorisation by click the Yes button.
%20-%20Copy.png?cb=2b24dd48d73904be6197372ca998a24c)
-
After successful authorisation the MS Windows button will change colour to green.
Outgoing email
Fill out the fields in the Outgoing mail SMTP server section.
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Server |
smtp.office365.com |
|
Name |
Enter you email address. |
|
Password |
Enter your password. For two-step verification you need to generate the App Password. Generate one and enter it here. |
|
Port |
587 |
Azure Security Setting for Microsoft Office 365
Azure Security Setting for Microsoft Office 365
Scenario 01
Screen 01
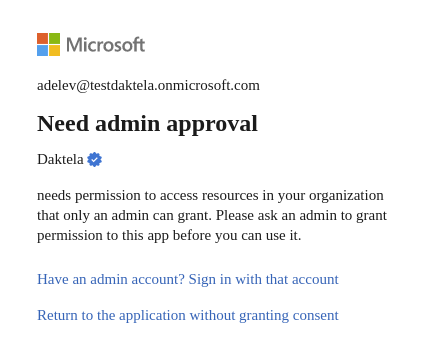
Screen 02
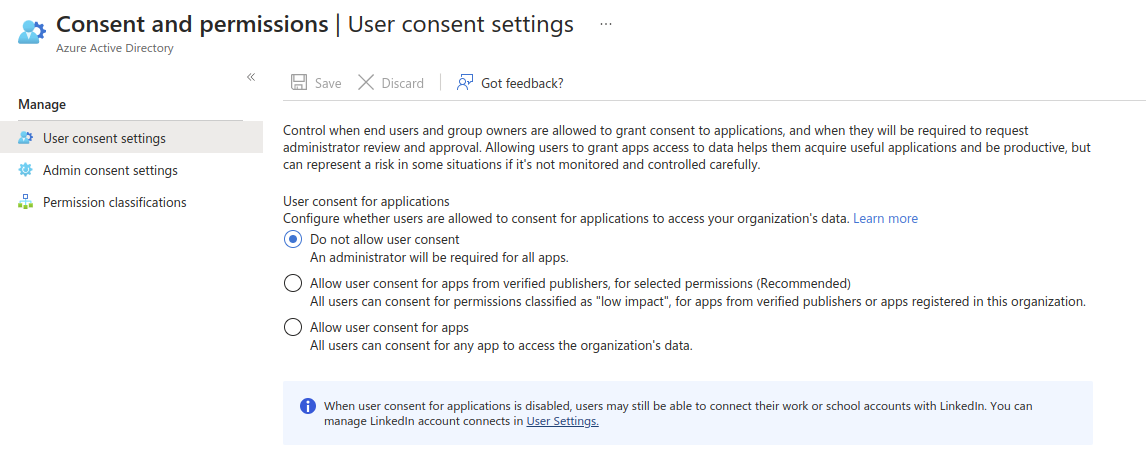
Screen 03
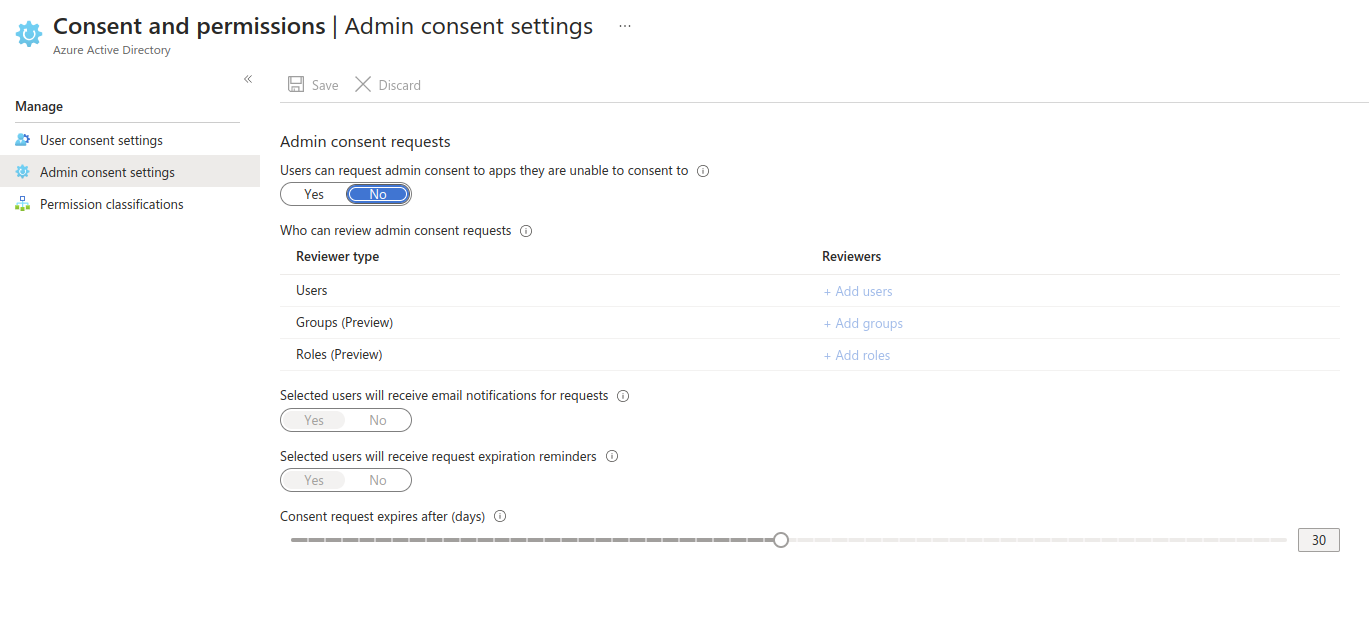
Scenario 2
Screen 01
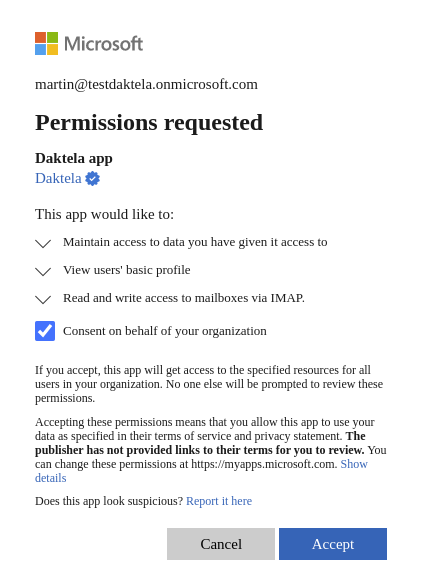
screen 02

screen 03
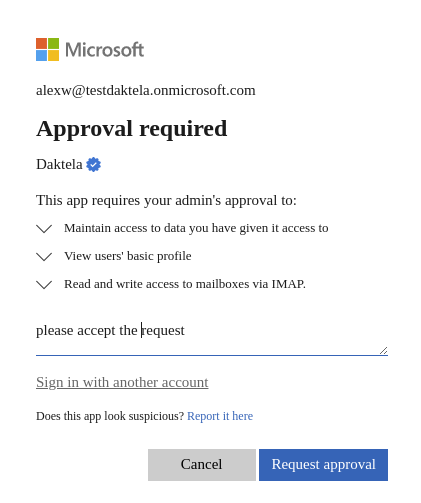
screen 04
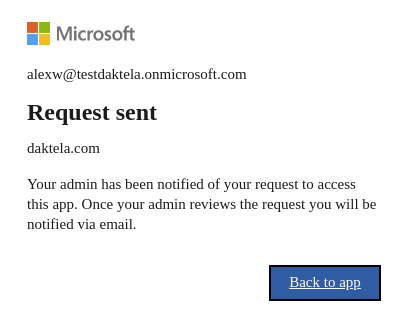
Screen 05
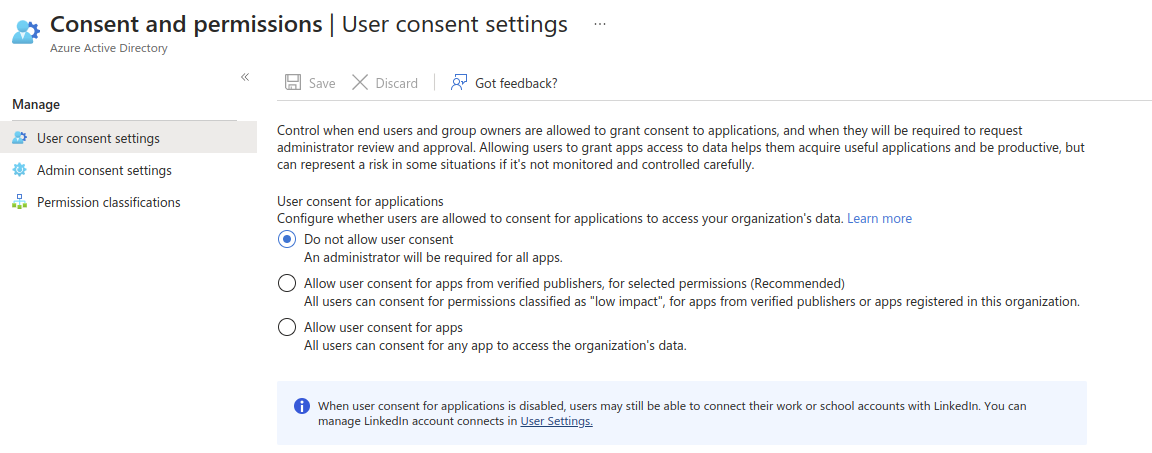
screen 06
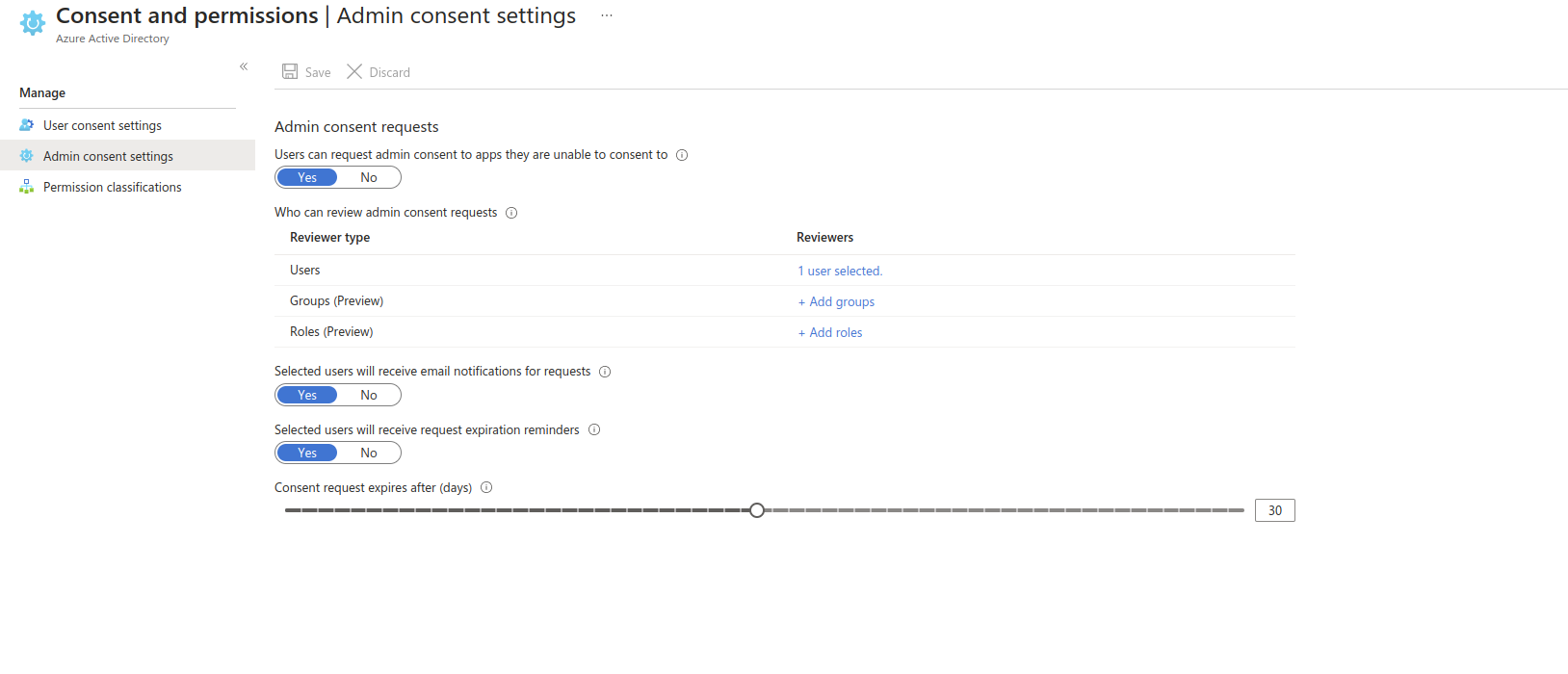
screen 07
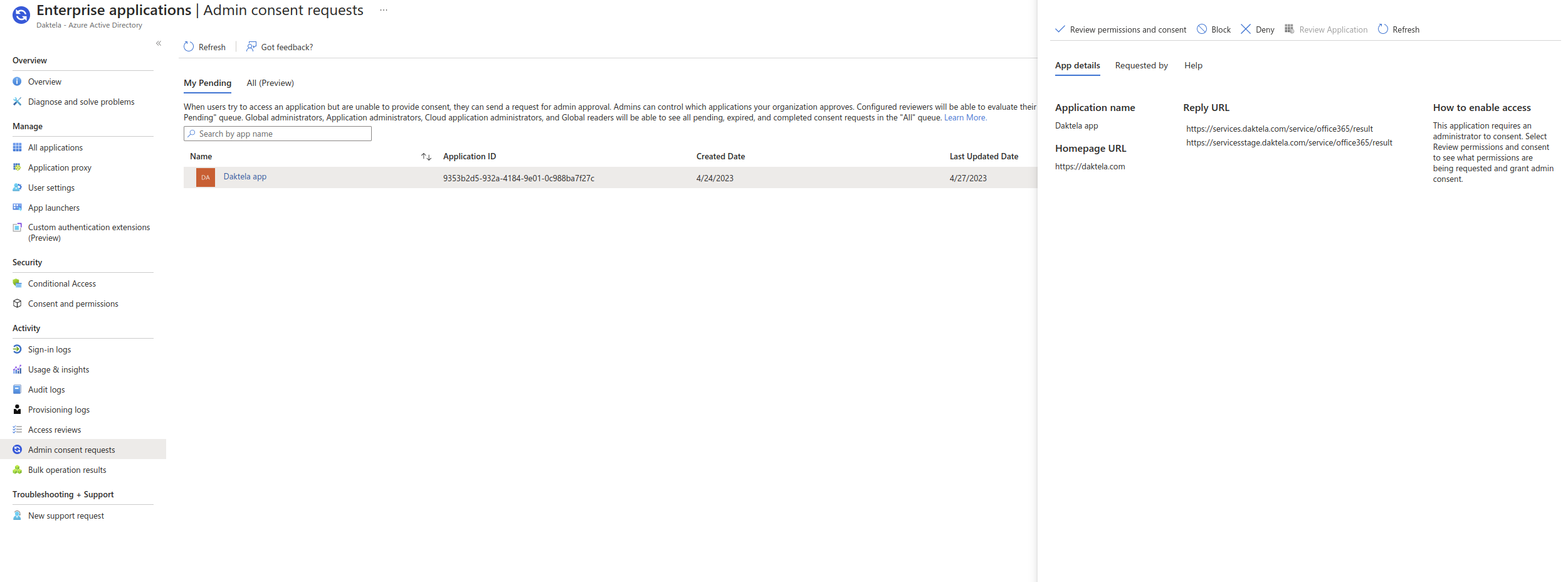
Azure Email Tenant Application
Azure Email Tenant Application
How to get authorisation data
-
Enter any title into the "Title" field below.
-
Log in at portal.azure.com as an admin user.

-
Open the menu on the left and go to "Entre ID".

-
Copy "Tenant ID" from overview page and paste it into the "Tenant ID" field in the Daktela integration.
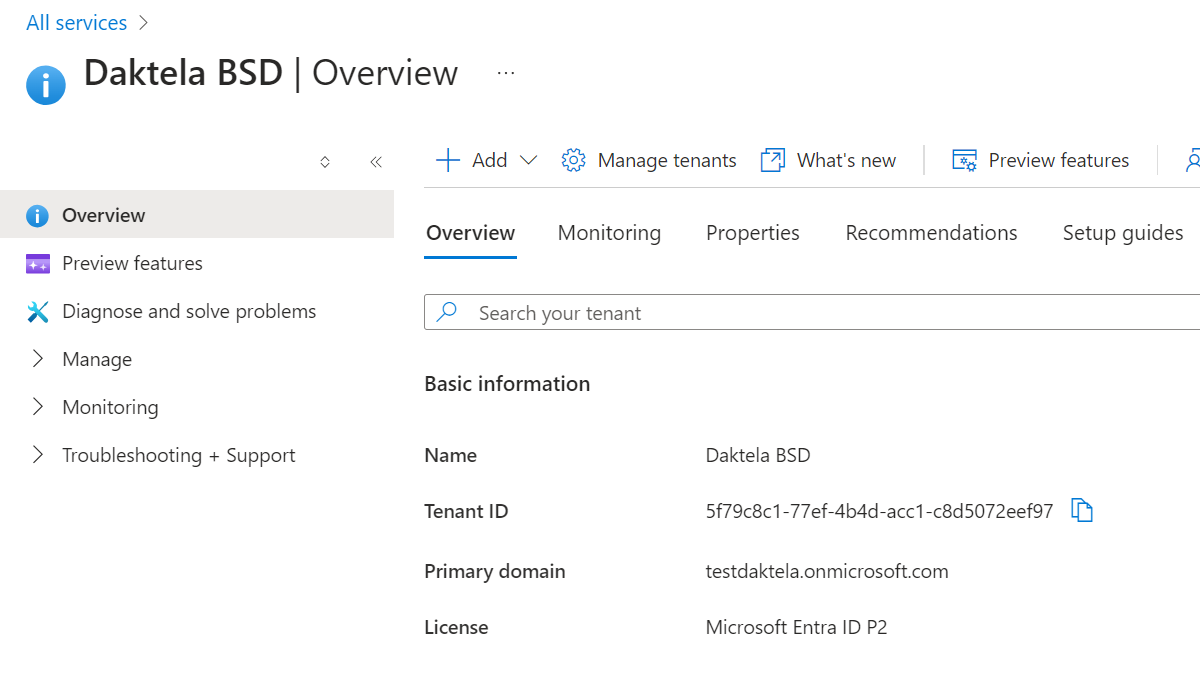
-
Open "Manage -> App registrations" from the menu, then click "New registration".
-
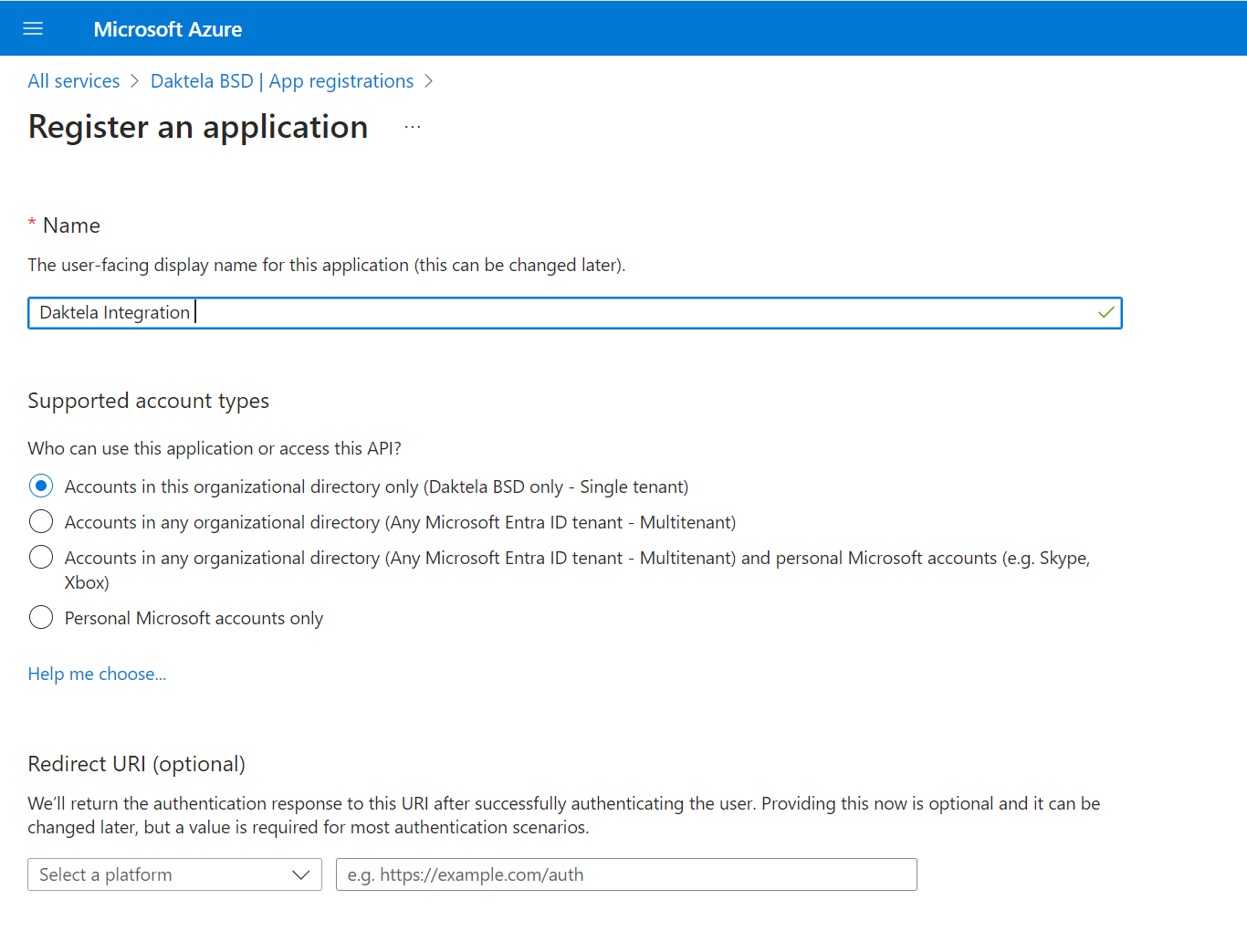
Enter a name for your application, e.g. "Daktela integration", and click "Register".
-
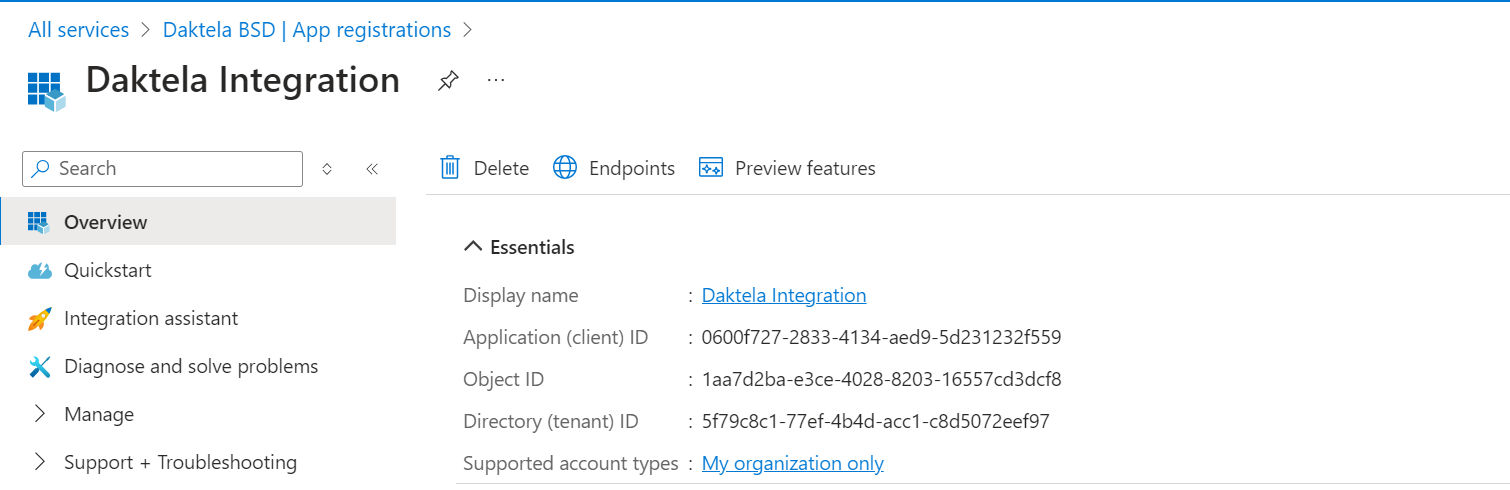
Copy the "Application (client) ID" and paste it into the "Application ID" field in the Daktela integration.
-
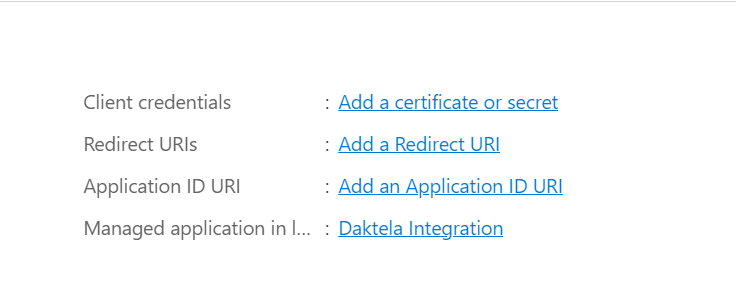
In the details of the app you created in the previous step, go to "Certificates & secrets" in the menu on the right, then click "New client secret" under "Client secrets".
-
Enter a short description and select the longest expiration option, then click "Add".
-
Copy your secret "Value" and paste it into the "Client secret" field in the Daktela integration.
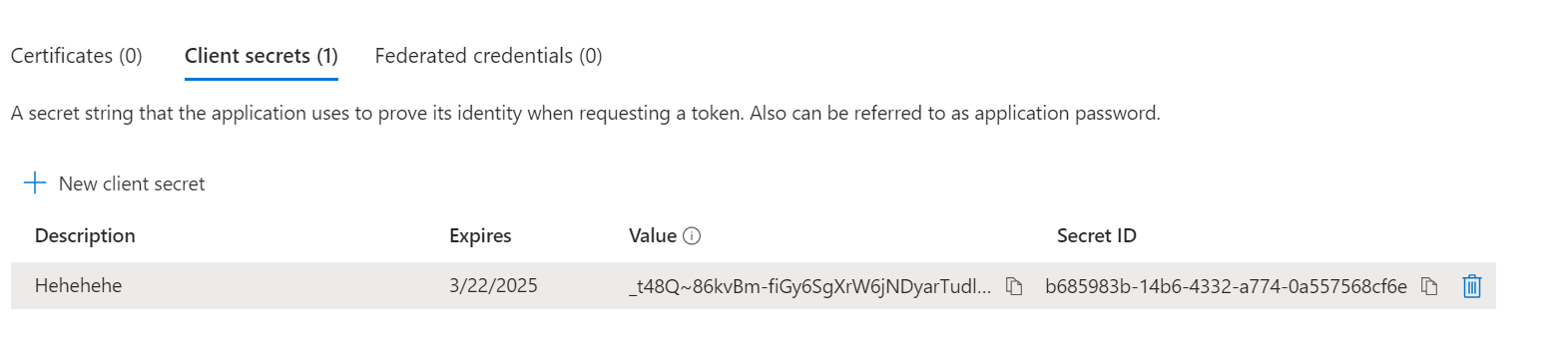
-
Go to "API permissions" and add next application permissions
-
For incoming: Mail.Read Mail.ReadBasic Mail.ReadBasic.All Mail.ReadWrite
-
For outgoing: Mail.Send
-
-
Click "Grant admin consent"
Incoming Email Process
Incoming Email Process
Incoming emails, email routings, tickets, categories, views – how are they all connected?
When you receive an email at an address that you have linked with Daktela, it will be routed according to the chart below:
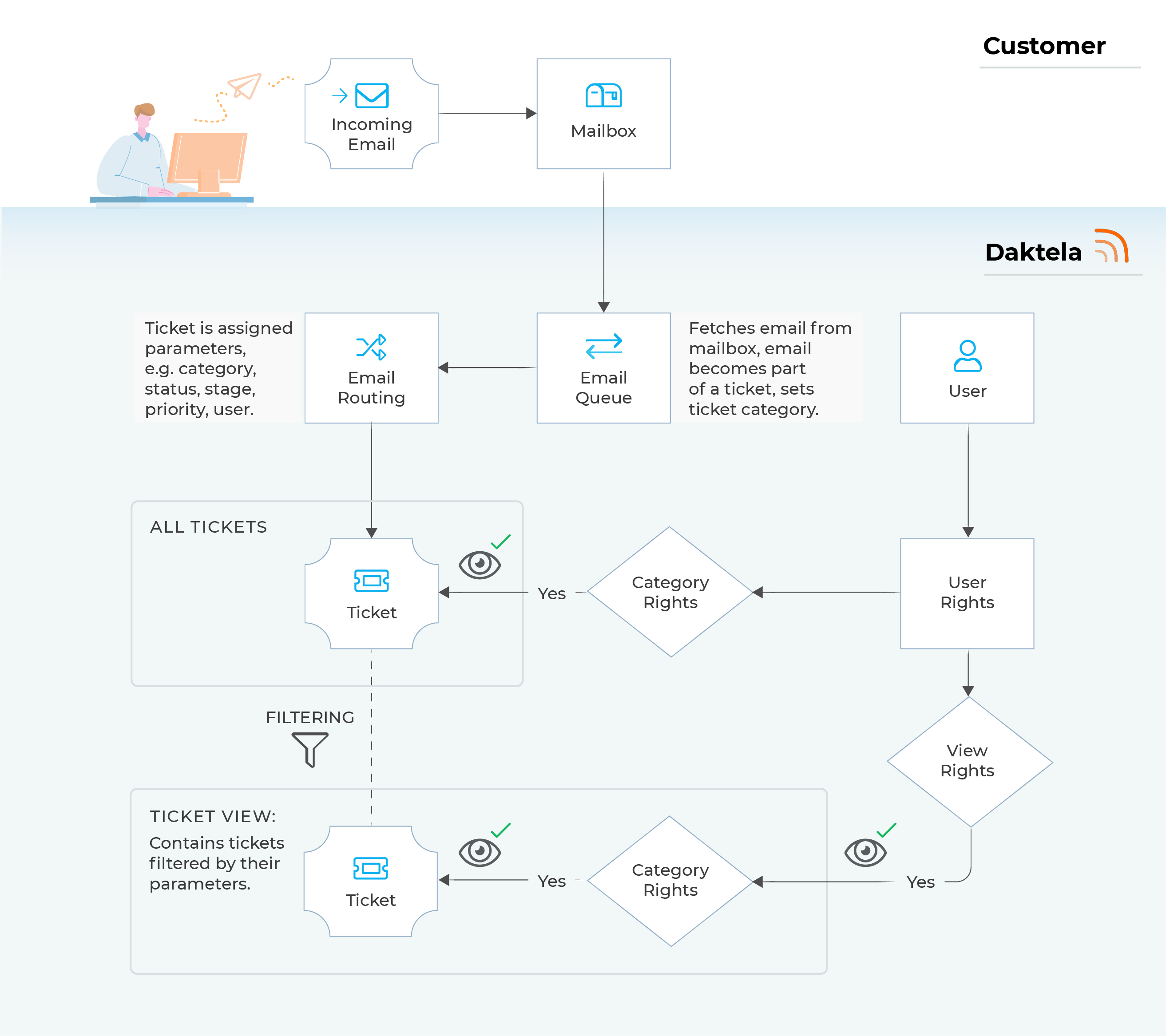
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Incoming email and Mailbox |
You receive an email on your mail server. |
|
Email queue |
The mail server is synchronised with Daktela via an email queue. The incoming email becomes a part of a ticket (a new ticket if it is a new email or an existing ticket it the email is a reply). The queue sets the ticket category. |
|
Email routing |
In email routings, you can define conditions under which further ticket parameters will be set. If none of the conditions are met, new tickets will only have a category set and the rest of the parameters will be blank. The category set in email routings will overwrite the category set in the email queue. |
|
Ticket in All Tickets |
The ticket is visible in All tickets to users that have rights to the ticket's category. |
|
Ticket in another Ticket View |
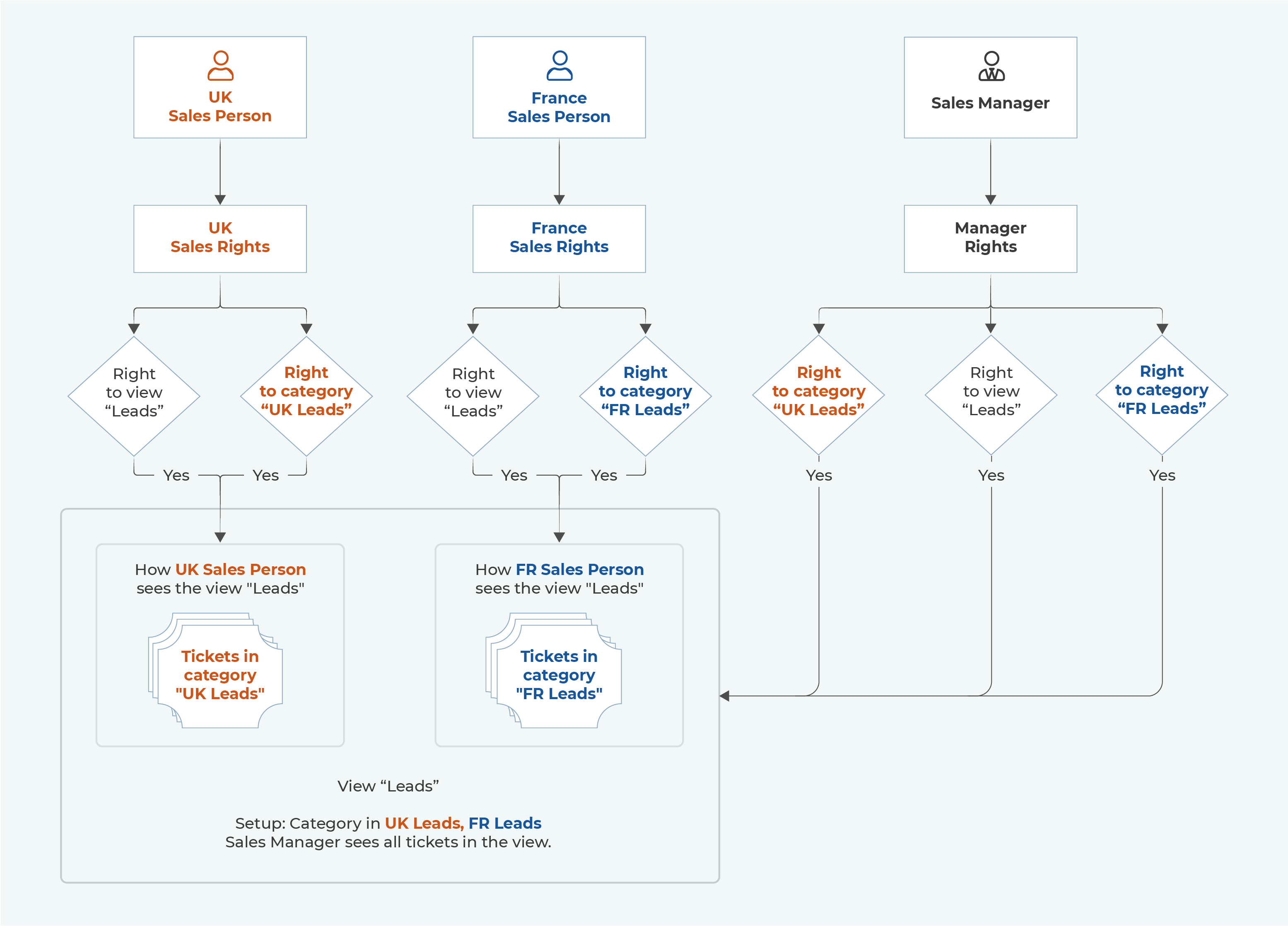
A ticket view is a predefined ticket filter that groups together tickets based on their parameters (either set up in the email queue or email routings, or selected manually in the ticket). Consequently, a single ticket can be part of several views – e.g. one based on its category, one based on its status and one based on its age since the last activity. A view is accessible to all users that have rights to it. However, to view the tickets contained in the view, they must still have rights to their categories. This means that different users can see different tickets in the same view. In the example below, there are 3 users that all have rights to the view "Leads".
|
